
Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) is gaining attention in the field of longevity and wellness. But what about its safety? With a surge in sales and sometimes exaggerated promises, it’s crucial to understand the potential side effects of this dietary supplement.
[Insert widget: YouTube Video] ID: w1X2Y2G6czs
[Insert widget: Calculator/Quiz] Type: NAD+ Profile Assessment and Personalized Score
[Insert widget: Alert/Box] Title: Key Takeaways. Key points: Overall safety (8.2% minor effects), Age-appropriate dosage (200-1200mg), Refrigeration required, Mild gastrointestinal effects, Caution for pregnant women/kidney disorders.
What is NAD⁺
[Insert Diagram]
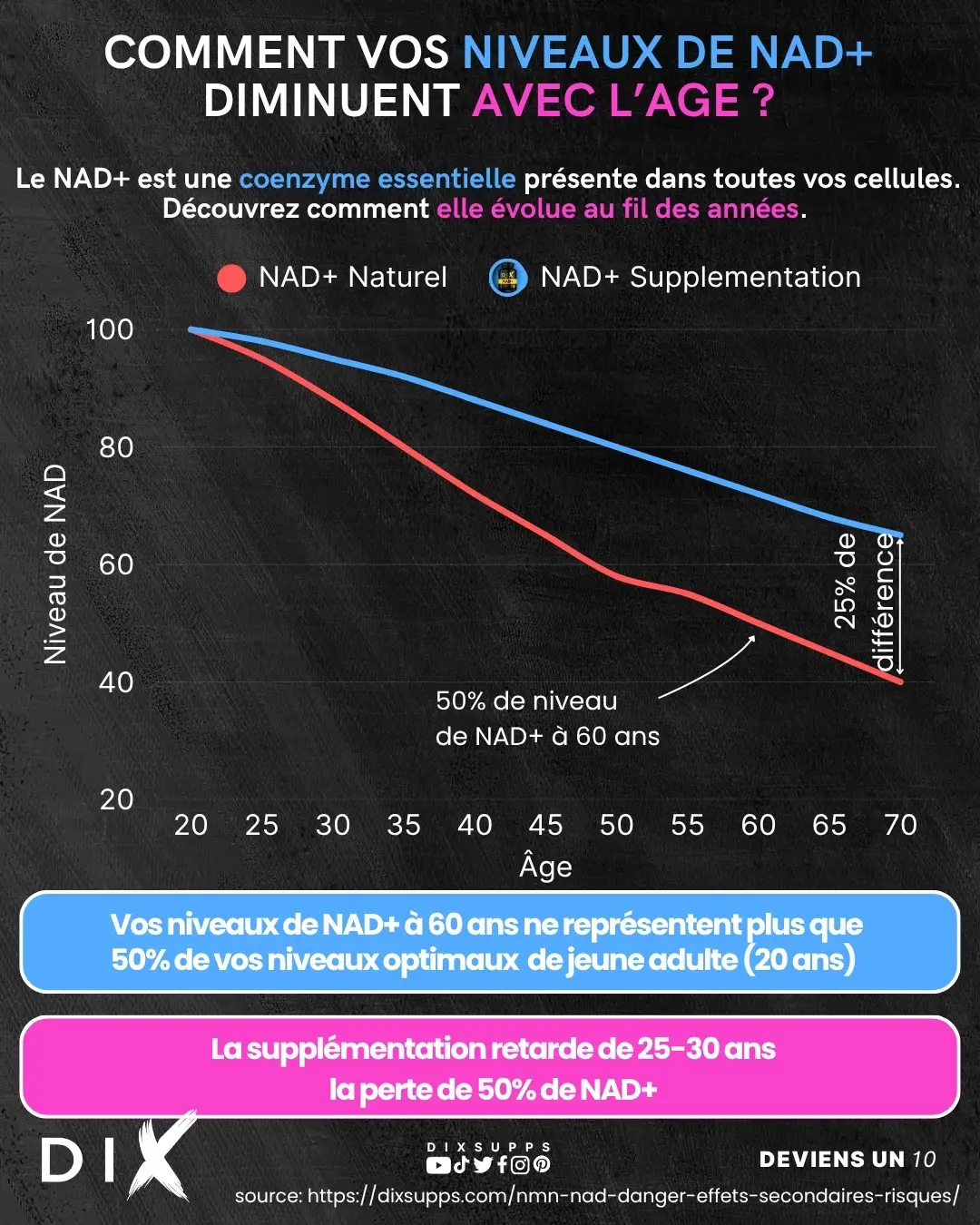
NAD⁺ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) is an essential coenzyme present in all our cells. It is involved in energy production, DNA repair, metabolism regulation, and maintaining proper cellular function.
As we age, NAD⁺ levels naturally tend to decrease, which may contribute to certain signs of aging and a decline in metabolic performance.
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is one of the natural precursors of NAD⁺. It is produced by the body and found in very small amounts in certain foods like avocado, broccoli, cabbage, or tomato.
One would need to consume a large quantity of these foods to obtain even a few milligrams of NMN.
This is why supplementation with NAD⁺ precursors has become popular in recent years. NMN, for example, is often offered in capsule or powder form, with dosages typically ranging from 50 to 500 mg per intake.
Research suggests that increasing NAD⁺ levels could have beneficial effects on mitochondrial function, insulin sensitivity, and certain aging markers. However, human clinical data is still limited, and long-term effects require further studies.
For now, short-term trials indicate good tolerance, with no major adverse effects observed at commonly used doses.
Scientific Research on NAD⁺ and its Precursors
In recent years, several studies have focused on NAD⁺ and its precursors like NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) and NR (nicotinamide riboside).
Research is generally reassuring. A systematic review published in 2024, involving over 400 participants, concluded that supplementation with NAD⁺ precursors was well tolerated and no serious adverse effects were observed, even at doses ranging from 250 to 1000 mg per day.
Notable studies include:
- Yi et al. (2023): 80 healthy adults received up to 900 mg of NMN per day for 60 days. Result: a measurable increase in blood NAD⁺ and no notable side effects.
- Trammell et al. (2016): the first major study on NR, demonstrating that it effectively increases NAD⁺ levels in the body, with excellent tolerance even at high doses (up to 1000 mg per day).
- Okabe et al. (2022): 30 volunteers took 250 mg of NMN for 12 weeks with no abnormal clinical signs.
- Yoshino et al. (2021): in prediabetic women, 250 mg of NMN per day improved insulin sensitivity without causing adverse effects.
Reported side effects in these studies are very rare and mild: slight nausea, temporary headaches, or digestive discomfort. Nothing comparable to the side effects sometimes observed with other supplements.
On the other hand, NADH (the reduced form of NAD⁺) has also been tested in humans, particularly for its effects on fatigue and concentration. Clinical trials show good tolerance up to 25 mg per day, with no notable issues reported.

Side Effects of NAD⁺ and its Precursors
Available clinical studies to date are very reassuring. Among more than 400 participants studied across various trials on all molecules, only a few isolated cases of mild side effects have been reported, and none were considered serious. Most of these effects were temporary, often unrelated to supplement intake.
Most Frequently Reported Side Effects
Common minor effects observed in studies:
- Mild digestive issues (abdominal discomfort, loose stools, transient nausea)
- Mild headaches
- Transient fatigue or sensation of warmth
- Temporary flu-like symptoms
It is interesting to note that in several studies, including Okabe et al. (2022), these symptoms appeared at similar frequencies in the placebo group, suggesting they are not necessarily related to supplementation.
Distinction Between Supplementation-Related and Unrelated Effects
Researchers also took care to distinguish effects truly attributable to NAD⁺ from those due to other factors. For instance, in some studies, isolated cases of acne or hypertension were observed, but no clear causal relationship was confirmed.
Finally, even at high doses, up to 1200 mg per day in some clinical studies, no serious side effects have been observed. Researchers thus conclude that NAD⁺ precursors have an excellent safety profile for short-term use.
How to Use NAD⁺ Safely
The safety of enzyme use primarily relies on two elements: adhering to appropriate dosages and proper product storage. Clinical studies published so far have established dosage ranges considered safe for daily use.
Dosages Generally Observed in Studies
Research shows good tolerance for doses ranging from 250 to 900 mg per day depending on the molecule and the individual’s profile. Some trials have even used up to 1200 mg/day without observing serious side effects.
As a guideline, here are the dosage ranges frequently mentioned in scientific literature for supporting cellular metabolism:
- 30-40 years: 200 to 400 mg per day
- 40-50 years: 400 to 600 mg per day
- 50-60 years: 600 to 800 mg per day
- Over 60 years: 800 to 1000 mg per day
A simple alternative is to estimate the dose based on body weight: approximately 8 mg per kilogram of weight. (For example, for 70 kg = about 560 mg per day)
Populations requiring special precautions
Certain individuals should exercise particular caution before consuming these molecules:
- Pregnant or breastfeeding women (as a precautionary principle, since no clinical studies have yet been conducted on these populations)
- Individuals undergoing treatment for diabetes (these molecules may influence insulin sensitivity)
- Individuals with renal or hepatic insufficiency
Storage and timing of intake
Key points for storage:
- Store in a cool, dry place, ideally in the refrigerator
- Avoid prolonged exposure to heat and humidity
- Respect the expiration date indicated on the packaging
It is generally recommended to take NAD⁺ precursors in the morning, with a meal containing a source of lipids. This combination promotes better absorption and supports cellular energy throughout the day.
Other common questions about NAD⁺
Can NAD⁺ cause headaches?
A few isolated cases of headaches have been reported in some studies, but they were rare and often not directly linked to supplementation. The observed frequency was similar in placebo groups.
Can it be taken every day?
Yes. Clinical trials conducted on NR, NMN, and NADH confirm that daily intake is well tolerated over several weeks, without notable side effects.
Do these molecules affect sleep?
Taking them in the morning is generally recommended, as it supports energy production and cellular metabolism throughout the day.
However, some studies suggest that the timing of intake could slightly influence sleep. For example, research conducted by Kim et al. observed that taking it in the late afternoon could improve sleep quality in some elderly individuals. These effects remain mild and variable among individuals.
Are there any long-term risks?
To date, no long-term risks have been identified in human clinical studies. However, most trials have not exceeded 12 weeks, meaning that effects over several months or years remain to be better documented.
Longer animal studies, however, remain reassuring regarding overall safety.
Are there any known drug interactions?
No significant drug interactions have been identified to date. As a precaution, it is advisable to consult a healthcare professional before starting supplementation, especially if undergoing current medical treatment.
Should TMG (Trimethylglycine) be combined?
Some experts, including Dr. David Sinclair, suggest combining a source of TMG to support methyl group metabolism when increasing intake.
However, research remains limited and this combination is not considered essential at this time.

NAD⁺ DIX: safety and quality at the heart of our production
In view of the studies presented and the importance of the quality of NAD⁺ precursors to ensure effectiveness and safety, the choice of your supplement plays a determining role.
Our NAD⁺ DIX meets the highest quality standards mentioned in scientific publications. Every step of our production is designed to preserve the integrity of the ingredients and maximize their bioavailability:
- GMP and HACCP certification (ensuring strict manufacturing and traceability standards)
- Enzymatic production for optimal bioavailability and enhanced stability
- Independent laboratory tests on each batch to ensure 99.9% purity
- Complete absence of heavy metals, solvents, or chemical residues
- Hermetic packaging for ideal preservation, protected from heat and humidity
As clinical studies have shown, product purity is essential to ensure its effects on the natural production of NAD⁺ while minimizing any risk of side effects.
Our enzymatic manufacturing process, closer to the body’s natural mechanisms, ensures better assimilation and optimal tolerance.
Scientific publications
- “Efficacy and safety of β-nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation in healthy middle-aged adults: a randomized, multicenter, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group, dose-dependent clinical trial” (Major study on NMN safety at different doses) DOI: 10.1007/s11357-022-00705-1
- “Safety and anti-aging effects of nicotinamide mononucleotide in human clinical trials: an update” (Comprehensive review of NMN safety studies) DOI: 10.1016/j.advnut.2023.08.008
- “Improvement of physical performance parameters in patients taking nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN): A systematic review of randomized controlled trials” (In-depth analysis of safety and efficacy) DOI: 10.7759/cureus.65961
- “Oral administration of nicotinamide mononucleotide is safe and effectively increases blood levels of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide in healthy subjects” (Clinical study on oral administration safety) DOI: 10.3389/fnut.2022.868640
- “Effect of oral nicotinamide mononucleotide administration on clinical parameters and nicotinamide metabolite levels in healthy Japanese men” (First clinical study on NMN safety) DOI: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ19-0313
- “Effect of nicotinamide mononucleotide intake for 12 weeks on sleep quality, fatigue, and physical performance in older Japanese adults” (Study on long-term effects) DOI: 10.3390/nu14040755
